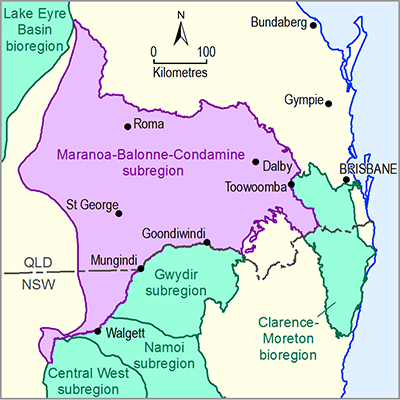
CSG and coal mining development in the Maranoa-Balonne-Condamine subregion targets the Walloon Coal Measures of the geological Surat and Clarence-Moreton basins. The main Great Artesian Basin (GAB) aquifers in the subregion, listed from shallowest to deepest, are the Bungil Formation, Mooga Sandstone, Gubberamunda Sandstone, Springbok Sandstone, Hutton Sandstone, Marburg Sandstone and Precipice Sandstone. The deeper sandstone aquifers of the Clematis Group and equivalent formations of the Bowen Basin are also recognised as GAB aquifers. Major aquitards in the subregion listed from shallowest to deepest are the Griman Creek, Wallumbilla, Orallo, Westbourne, Birkhead, Evergreen formations and Rewan Group (and their stratigraphic equivalents). Other than the GAB aquifers, the major aquifer systems in the subregion are the Cenozoic alluvial aquifers and the volcanic basalt aquifers along the eastern margin of the subregion. The Condamine Alluvium is the most significant and highly-developed alluvial groundwater system in the subregion. It is heavily used for groundwater supply predominantly for irrigation, but also for town water supply, domestic, stock, watering and industrial uses to a lesser extent. Significant aquifers are contained in the Main Range Volcanics in the east of the subregion and Cenozoic basalts that occur in the north of the subregion overlying the Bowen Basin. These basalt aquifers are used for irrigation, stock and domestic and town water supplies.
Coal resource development in the Maranoa-Balonne-Condamine subregion has the potential to directly affect the regional groundwater and surface water systems. Hydrological changes to the groundwater system can propagate through the alluvium and other aquifers to indirectly affect surface water – groundwater interactions in the aquifer outcrop and subcrop areas. Deep soil drainage and surface water – groundwater interactions in aquifer outcrop areas can also be affected by coal resource development, potentially affecting groundwater quality, aquifer properties, groundwater composition, flow (reduction), level and pressure. Potential changes to groundwater conditions include groundwater quality, aquifer properties, groundwater composition, flow (reduction), level and pressure in affected aquifers.
River basins in the subregion are the Border, Condamine-Balonne (including the Maranoa River), Fitzroy and Moonie rivers. Most river systems in the subregion are temporary. An exception is parts of the Dawson River, which receives baseflow contributions from rejected GAB recharge in the aquifer outcrop areas. Potential effects of changes to surface water – groundwater interactions associated with the management, treatment and disposal of water include changes baseflow to ephemeral watercourses following aquifer reinjection or changed surface water – groundwater interactions around mine pits. Potential effects of coal resource development in the Maranoa-Balonne-Condamine subregion on runoff and overland flow in surface water catchments and streams are changes to surface water quality, direction, flow, volume and zero-flow days, including changes to the magnitude, duration and variability of surface water flows.
Product Finalisation date
- 2.3.1 Methods
- 2.3.2 Summary of key system components, processes and interactions
- 2.3.3 Ecosystems
- 2.3.4 Baseline and coal resource development pathway
- 2.3.5 Conceptual model of causal pathways
- Glossary
- Citation
- Acknowledgements
- Contributors to the Technical Programme
- About this technical product
